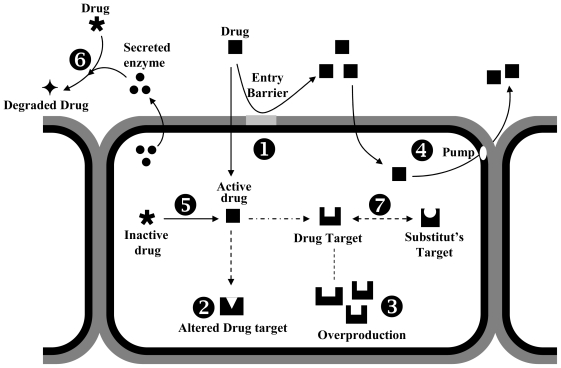
Figure 2.
Mechanisms by which fungal cells might develop resistance (adapted from Ghannoum and Rice, 1999) [67]. 1. The entry of the drug is prevented at the cell wall level. 2. The drug target is altered so that the drug cannot bind to the target. 3. The target enzyme is overproduced so that the drug does not inhibit the biochemical reaction completely. 4. The drug is pumped out by an efflux pump. 5. Some fungal enzymes that convert an inactive drug to its active form are inhibited. 6. The cell secretes some enzymes to the extracellular medium which degrade the drug. 7. The synthesis of an alternative enzyme, which replaces a drug target.