Figure 5.
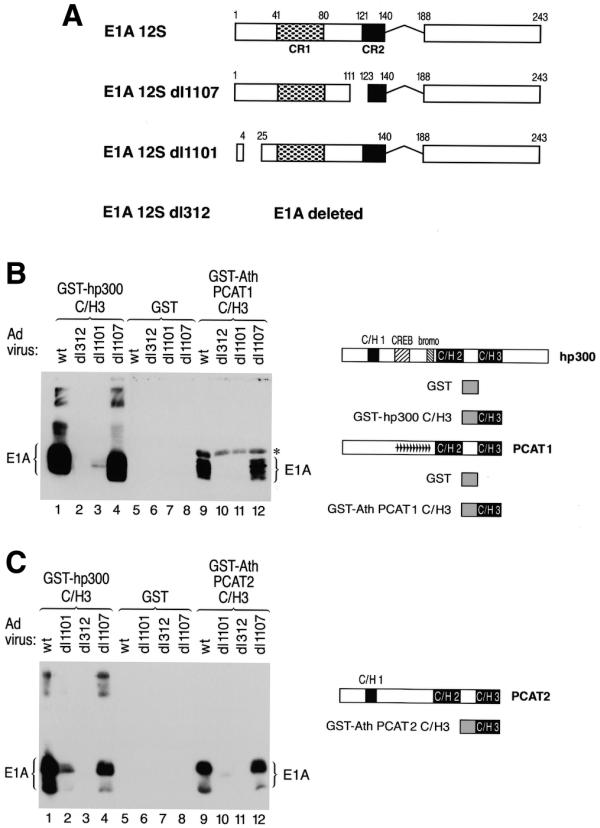
The C/H3 domain of PCAT1 and 2 specifically binds to E1A and discriminates between mutant E1A proteins in a manner recapitulating the binding pattern of human p300. (A) A schematic representation of the different adenovirus mutants used in the E1A binding assay is shown. The wild-type virus expresses wild-type 12S E1A, dl1107 expresses E1A carrying a mutation in conserved region 2 (CR2) of E1A (constituting part of the RB protein family binding site), dl1101 expresses a mutant form of E1A lacking amino acids 5–24 (constituting part of the p300 binding site) and dl312 does not express E1A at all due to a deletion in the early region removing the E1A gene. (B and C) Shown on the right are schematic representations of hp300 and PCAT1, 2 and the GST-C/H3 fusion proteins used for the E1A interaction assays. Purified GST proteins containing the C/H3 domain of hp300 [(B) and (C) lanes 1–4], of PCAT1 [(B) lanes 9–12], PCAT2 [(C) lanes 9–12] or GST alone [(B) and (C) lanes 5–8] were incubated with cell lysates prepared from U2OS cells infected with the indicated wild-type or mutant adenovirus. Bound E1A proteins were detected by western blot. The asterisk in (B) marks a non-specific background band visible in lanes 9–13. This band is due to binding of the secondary antibody to an E.coli protein copurifying with the GST–AthPCAT1–C/H3 fusion protein.
