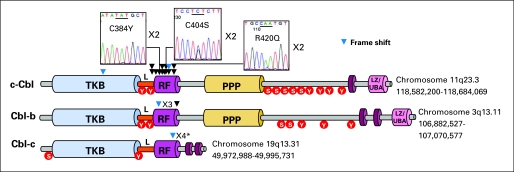
Fig 2.
Identification of variations in c-Cbl, Cbl-b and Cbl-c RING finger (RF) domain. Schematic representation shows the major domains of c-Cbl, Cbl-b, and Cbl-c, primarily the tyrosine kinase binding (TKB) domain, linker sequence (L), RF domain, proline-rich region (PPP), and leucine zipper (LZ)/ubiquitin-associated domain (UBA). Tyrosine and serine residues, represented by red circles, are phosphorylated by tyrosine kinases. Genomic DNA sequencing of all exons in c-Cbl, Cbl-b, and Cbl-c revealed the presence of (black arrow) missense and (blue arrow) frame shift mutations or frame shift polymorphisms in L or RF domain, except for a case with a mutation in the TKB domain. In c-Cbl, some basepair changes occured in a homozygous state because of UPD and resulted in the substitution of cysteine or arginine residues at positions 384 shared in two patients (C384Y), 404 in three patients (C404S/Y), and 420 in three patients (R420Q/P). (*) Frame shift polymorphism.