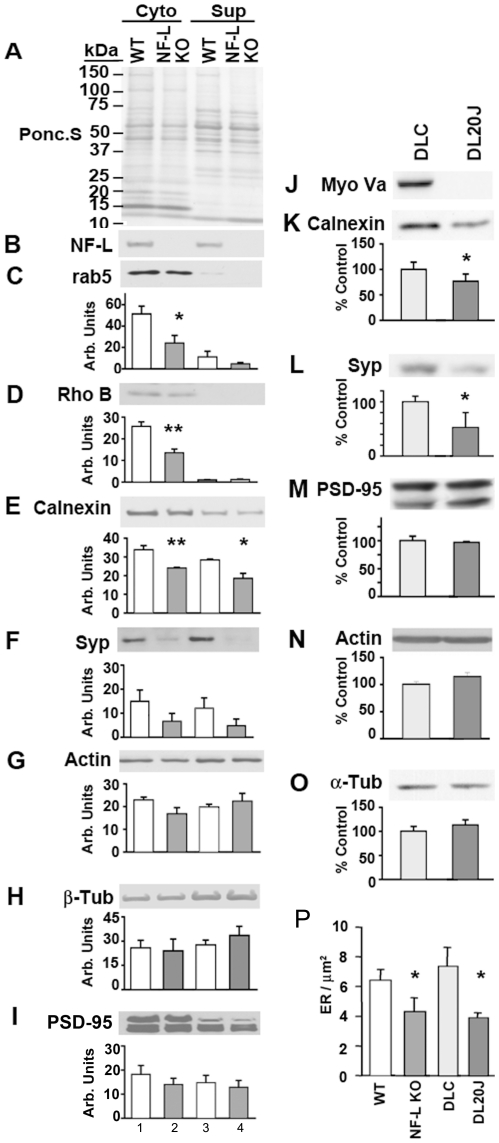
Figure 4. NF-network-dependent association of cellular organelles is reduced in NF-L null optic axons.
Cytoskeletal (lanes 1&2), and supernatant fractions (lanes 3&4) from WT (lanes 1&3) and NF-L null (lanes 2&4) optic nerves were resolved by SDS-PAGE, transferred to membranes, Ponceau S stained (A), immunoblotted with NF-L (B), Rab-5 (C), Rho B (D), calnexin (E), Synaptophysin (SYP, F), actin (G), tubulin (H), and PSD-95 (I) antibodies. Densitometric quantification of signals from immunoblots in panels C-F indicate significantly reduced amounts of Rab-5 (C), Rho B (D), calnexin (E), Synaptophysin (SYP, F), in NF-L null cytoskeletal fractions compared to controls while actin (G), tubulin (H), and PSD-95 (I) were not decreased in the same fractions. (n = 6 for each genotype of 5–6 month old mice). (J). Total extracts of optic nerves from DLC (dilute lethal control), and DL20J mice were immunoblotted with Myo Va, calnexin, Synaptophysin (SYP), actin, tubulin and PSD-95 antibodies. Quantitation data for calnexin (K), synaptophysin (SYP; L), PSD-95, actin and tubulin is shown in M-O. (P). Morphometric analysis indicate reduced density of ER vesicles in NF-L null and DL20J optic axons (n = 4 for 5–6 month old WT and NF-L null, and 17 day for DL20J and DLC). *p<0.05, and **p<0.01. Error bars represent SEM in all experiments.