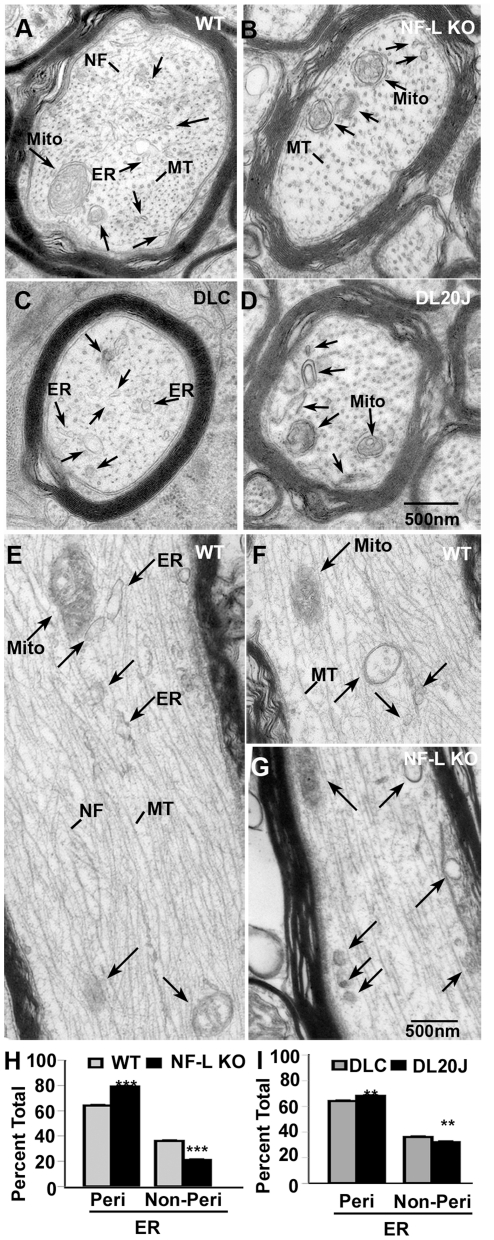
Figure 5. Loss of NF-L and Myo Va leads to increased peripheral distribution of ER vesicles in optic axons.
In cross sections of WT (A), and dilute lethal control (DLC) (C) axons a clear tubulo-vesicular and vesicular profiles distribute diffusely in the radial dimension (A&C) but are more peripherally distributed in NF-L null (B) and DL20J (D) optic axons (see arrows in A–D). In comparison to WT axons (E, F, see arrows), cellular organelles in NF-L null optic axons (G) are peripherally distributed along channels beneath the axolemma in longitudinal sections (see the arrows in G). Quantitative measurements of distribution of organelles within 100 nm from periphery of axons that are larger than 1 µm demonstrate that increased peripheral distribution of ER in both NF-L null (H) and DL20J (I). (n = 5 animals for 6-month old WT and NF-L null, and 17 day DL20J and DLC). **p<0.01, and ***p<0.001. Error bars represent SEM. NF: neurofilaments; MT: microtubules; Mito: mitochondria; Peri: peripheral; Non-peri: non-peripheral.