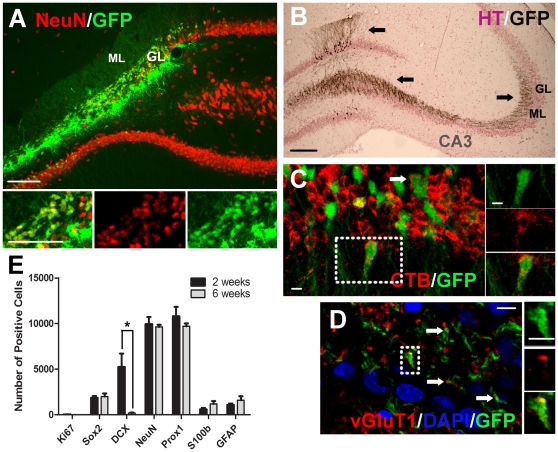
Figure 4. Most of the transplanted primary DG cells become DG granular neurons in-vivo.
DG cells were isolated from neonatal GFP rats and transplanted immediately after isolation. (A) Example of a GFP+ cell transplant in the hippocampus 6 weeks after grafting. Note that the grafted cells have substantially replaced missing NeuN+ cells in the granular layer. (B) Immunostaining of GFP in grafted cells detected with DAB (black). The section was counterstained with haematoxylin (HT) (purple) to detect cell nuclei. Note the substantial projection of transplanted neurons to the target CA3 region and intense ramification therein, as well as well developed dendritic projections into the molecular layer. (C) Retrograde transport of tracer cholera toxin B (CTB) injected into CA3 confirming this projection. (D) Image showing the expression of the pre-synaptic vesicular glutamate transporter 1 (vGluT1) on the axon terminals of grafted cells. (E) Total number of grafted cells per animal expressing different markers at 2 and 6 weeks (mean ± SEM, n = 4–5), *p<0.05. Note that the majority of cells are positive for NeuN and Prox1. Scale bar = 100 µm for A–B; scale bar = 10 µm for C–D.