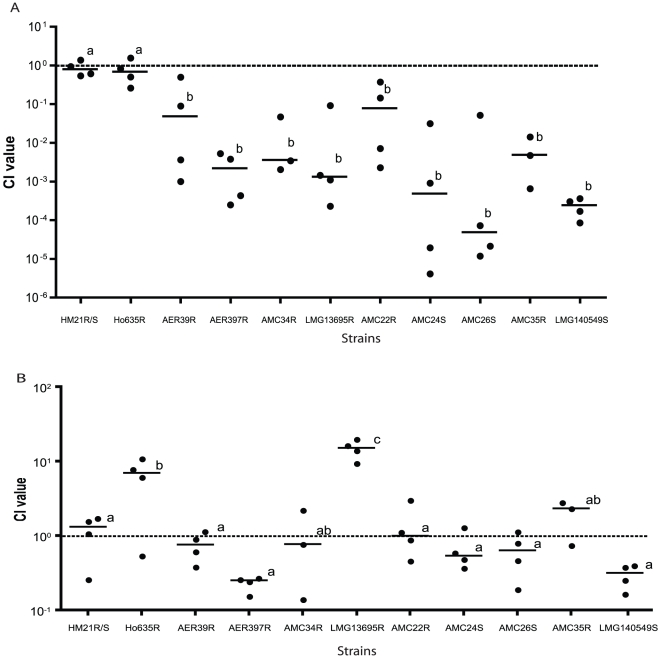
Figure 1. Symbiotic competence of AVG isolates and ability to grow in blood.
(A). The ability of AVG isolates to colonize the leech. Spontantous antibiotic resistant isolates were coinoculated with the competitor strain (HM21R or HM21S) in a 1∶1 ratio. The antibiotic resistance of the strain is indicated by “R” for rifampin resistant and “S” for streptomycin resistant. The CI [(testoutput/competitorout)/(testinput/competitorinput)] was calculated. Each point represents the CI value from a single competition assay. A CI of 1 (dashed line) indicates that the test strain and competitor strain colonize to equal levels. A CI below 1 indicates that the test strain is outcompeted and has a colonization defect. The CI for each animal is shown. Horizontal lines represent median CI values. Strains with common letters are not statistically different from one another as determined by one-way ANOVA with Tukey's post-hoc test, P<0.05. (B). Blood was coinoculated with an AVG isolate and the competitor strain (HM21R or HM21S) in a 1∶1 ratio. The CI was calculated. A CI of 1 (dashed line) indicates that the test strain and competitor strain proliferate to equal levels. A CI below 1 indicates that the test strain is outcompeted and has a defect in its ability to grow in blood. Horizontal lines represent median CI values. Strains with common letters are not statistically different from one another as determined by one-way ANOVA with Tukey's post-hoc test, P<0.05.