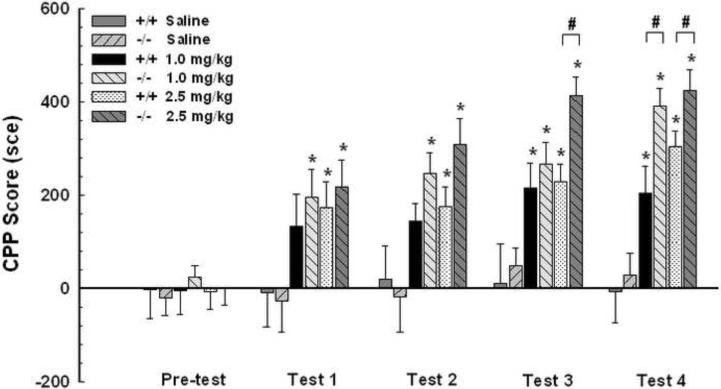
Fig. 1.
D3 receptor mutant mice show heightened CPP acquisition compared to wild-type mice. Three groups of D3 receptor mutant (−/−) and wild-type (+/+) mice received either cocaine (1 mg/kg, n=17 and 14 each; or 2.5 mg/kg, n=18 and 19 each) or saline (n=12 and 13 each) injections on alternative days, and were confined to specific compartments in a biased design. These mice were tested for place preference without injections. Both D3 receptor mutant and wild-type mice showed CPP acquisition induced by 1 and 2.5 mg/kg doses of cocaine but not by saline. Moreover, D3 receptor mutant mice exhibited higher CPP acquisition than wild-type mice at both doses of cocaine. Results represent mean ± SEM time spent on the drug-paired side minus that on the saline-paired side. *p<0.05 compared with the saline mouse group of the same genotype within the same test. #p<0.05 compared between two genotypes at the same cocaine dose and test.