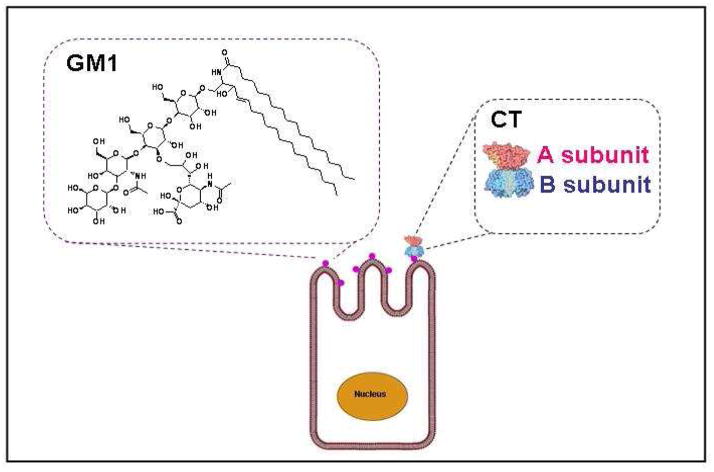
Scheme 1. Structure of the GM1 ganglioside found on intestinal epithelial cells and binding of cholera toxin (CT) to the target cells.
GM1 gangliosides, located on the surface of the targeted cells, are the known ligands that facilitate binding and internalization of CT. N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc), N-acetylneuraminic acid (Neu5Ac), glucose (Glc), and galactose (Gal) residues comprise the pentasaccharide moiety of the GM1 ganglioside facilitate interaction with the B subunit of cholera toxin (CTB).