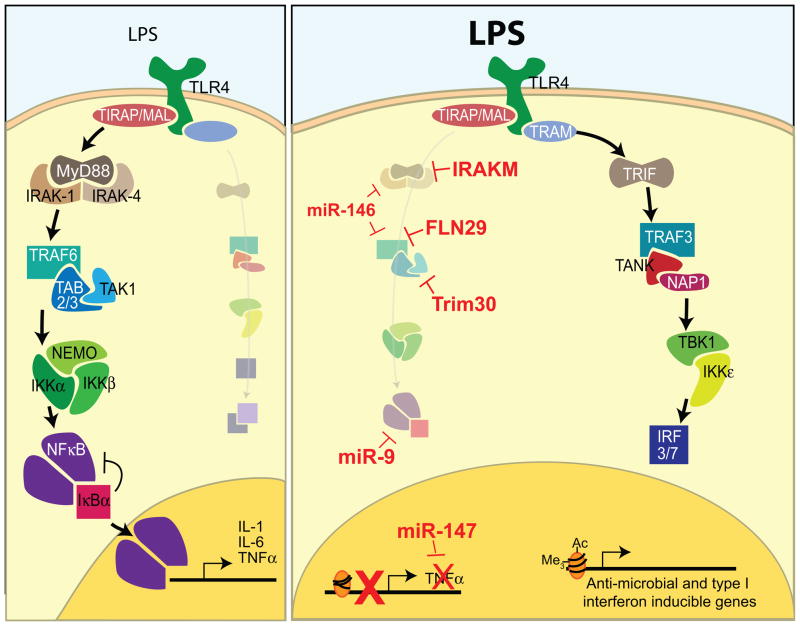
Figure 2.
Mechanisms of endotoxin tolerance. Left: Model of the primary TLR4 signaling cascade initiated in response to a low dose of LPS. Signaling commences through the MyD88 adaptor leading to NFκB activation producing a low level inflammatory response. Evidence suggests that this primary signaling cascade is required to induce a “tolerized” state. Right: Schematic of the TRIF-dominated response of TLR4 in endotoxin tolerance. Many inhibitors are in place to reduce MyD88 signaling and NFκB activity. The mechanisms that are utilized to create this reprogrammed TLR response include targeted inhibition of signal transduction (IRAKM, FLN29, TRIM30), microRNAs that regulate post transcriptional gene regulation (miR-9, 146, 157), and chromatin remodeling that promotes or suppresses gene expression.