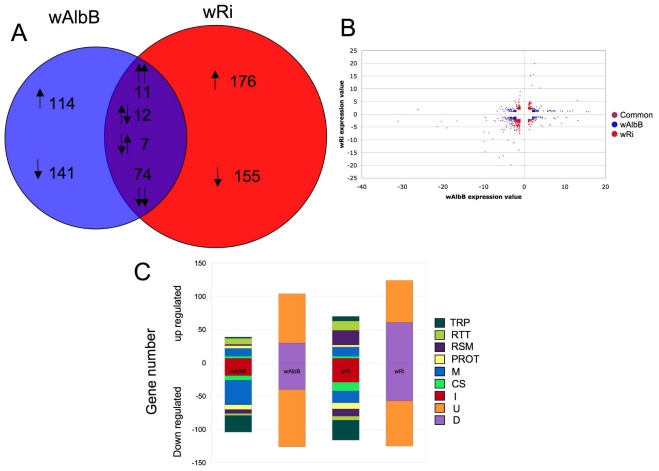
Figure 1. Anopheles gambiae gene regulation in response to Wolbachia infection.
A. Venn diagram of 690 Anopheles transcripts which display differential expression due to wAlbB or wRi infection. 104 transcripts were common to both strains, while 389 were down regulated and 320 up regulated due to Wolbachia infection. B. Scatter plot of regulated significant genes (>2 fold regulation; False discovery rate P value <0.05). Blue dots represent significant genes regulated by wRi only, red regulated by wAlbB only and purple, genes commonly regulated. C. Number of genes in each functional classes class up or down regulated in response to either wAlbB or wRi infection. Genes were classified into groups; transport (TRP), replication, transcription and translation (RTT), redox, stress and mitochondrial (RSM) proteolysis and digestion (PROT), metabolism (M) cytoskeletal and structural (CS) and immune (I) depicted in the first column, and diverse (D) and unknown (U), in the second column.