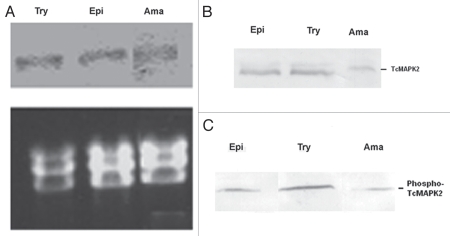
Figure 4.
Developmental studies of TcMAPK2 in three forms of T. cruzi. (A) Northern blot analysis of T. cruzi. Try (trypomastigotes), Epi (epimastigotes) and Ama (extracellular amastigotes). Top panel shows TcMAPK2 probe hybridization signals (∼4 kb) of total RNAs from three life forms of T. cruzi. Bottom panel shows Ethidium bromide-stained gels demonstrated the equal loading of T. cruzi ribosomal RNA and confirmed the integrity of the samples. There was no change in the level of mRNA among three forms of T. cruzi. (B) Immunoblot analysis of T. cruzi using anti-TcMAPK2. The results indicated that the TcMAPK2 protein level was at the same level in trypomastigotes and epimastigotes but TcMAPK2 protein level in amastigotes is lower than that in other forms. (C) Immunoblot analysis of T. cruzi using anti-phospho-TcMAPK2. Trypomastigotes have highest level of phospho-TcMAPK2, followed by epimastigote and then extracellular amastigotes. Based on the data from analysis of densitometry, the ratio of phospho-TcMAPK2 vs. TcMAPK2 is two folds higher in trypomastigotes as compared to that of epimastigotes and amastigotes.