Fig. 4.
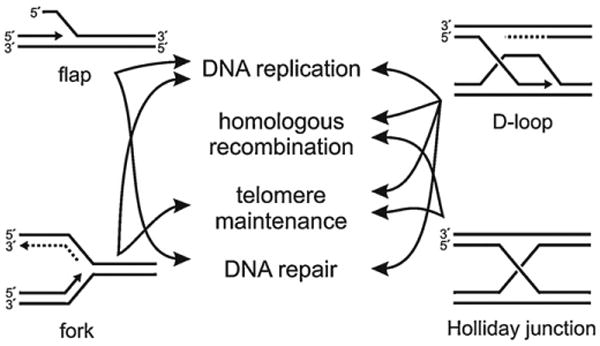
Inferred RECQ helicase substrates and their roles in DNA metabolism. The common model substrates depicted in Fig. 3 and used to define RECQ helicase biochemical activities have direct counterparts in cellular DNA metabolism. RECQ helicases are able to unwind and release DNA flaps (upper left); promote replication fork progression, regression or remodeling (lower left); release an invading 3′ DNA tail in a D-loop (upper right); and branch migrate and, in the case of BLM in conjunction with topoisomerase IIIα, resolve separate DNA duplexes joined in a Holiday junction (lower right).
