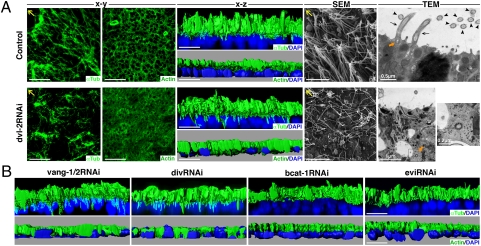
Fig. 5.
Defective positioning of the cilial actin network in dvl-2, vang-1/2, and div RNAi planarians. (A) Anti-αTub and anti-Actin immunostaining of control and dvl-2 RNAi planarians. The x-y and x-z confocal projections are shown. SEM of the planarian epidermis showing the differences in cilial density and orientation. Ultrastructural analysis by TEM of epithelial cells of the planarian epidermis. Several cilia anchored to the apical membrane can be seen in longitudinal (black arrows) and transverse (black arrowheads) sections in a control planarian. A basal body is indicated with an orange arrow. A basal body found isolated in the cytoplasm, outside a vesicle, is shown at two different magnifications in the image corresponding to a dvl-2 RNAi planarian (orange arrow). Yellow arrows indicate anterior. (B) Anti-αTub and anti-Actin immunostaining of vang-1/2, div, bcat1, and evi RNAi planarians. The x-z confocal projections are shown. DAPI nuclear staining is shown in blue. bcat1, Smed–β-catenin1; div, Smed-div; dvl-2, Smed-dvl-2; evi, Smed-evi; αTub, α-tubulin; vang-1/2, Smed-vang-1/2. (Scale bar: 10 μm unless otherwise indicated.)