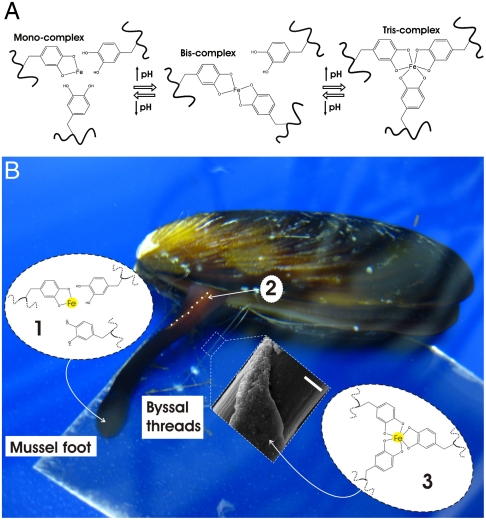
Fig. 1.
Mussel-inspired Dopa-Fe3+ cross-linking. (A) The pH-dependent stoichiometry of Fe3+-catechol complexes. (B) Schematic of proposed cross-linking mechanism of byssal thread cuticle: (i) Production and storage of mfp-1 and Fe3+ in specialized cells of the epithelium lining the ventral groove of the mussel foot. Low pH (≤ 5) ensures mono-catechol-Fe3+ complexes (no cross-linking), (ii) Secretion and self-assembly of cuticle with whole mussel thread in the ventral groove (outline of part of ventral groove indicated with dashed white line), (iii) Seawater exposure (pH ∼8) of nascent byssal thread drives immediate cuticle cross-linking via bis- and/or tris-catechol-Fe3+ complexes (insert shows scanning electron micrograph of mussel thread with partial cuticle on top of fibrous core) (Scale bar, 20 μm).