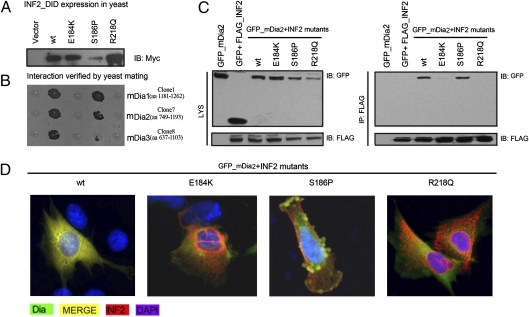
Fig. 5.
Effect of disease-causing INF2 mutations on mDia interaction. (A) The expression of WT and mutants of INF2_DID in AH109 was detected by immunoblotting with an antibody against Myc-Tag. The plasmids (pACT2) carrying candidate proteins were transformed Y187 yeast strain. (B) The transformants were mated and dotted on QDO agar plates. The interactions between INF2_DID (WT) and the candidate protein fragments of mDia1, mDia2, and mDia3 were tested (column labeled WT), as were the interactions of INF_DID mutants (E184K, S186P, and R218Q) with the captured fragments. (C) 293T cells were cotransfected with plasmids encoding GFP-mDia2 and FLAG-INF2 mutants. The cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-FLAG antibody. Immunoprecipitation of INF2 with the E184K and R218Q mutants did not bring down mDia2, in contrast to WT and S186P mutants. (D) Podocytes were cotransfected with plasmids encoding GFP-mDia2 and FLAG-INF2 mutants and subjected to double staining of FLAG and GFP-tagged proteins (red, FLAG; green, GFP; yellow, merged).