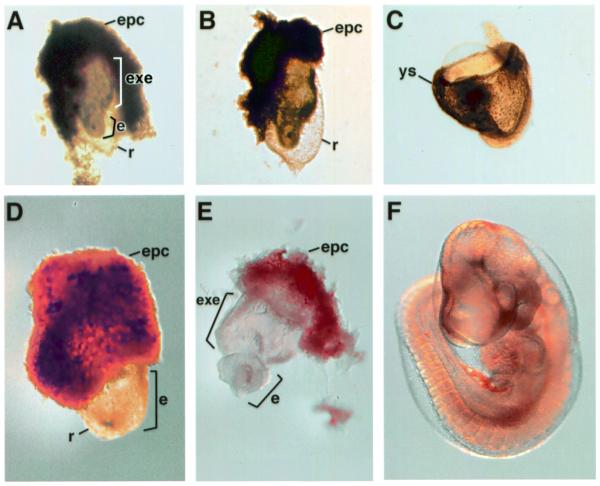
Figure 2.
HdhSTOP/– embryos resemble Hdh–/– embryos. Examples of Hdh–/– (A and D), HdhSTOP/– (B and E), wild-type (C) and Hdh+/– (F) embryos at E8.5 (A–C) and E9.5 (D–F) are shown. The embryonic portions (e) of the Hdh–/– and HdhSTOP/– mutants are stubby and retarded in development in comparison to their wild-type counterparts. The extraembryonic (exe) portion of the mutant embryos and the yolk sac (ys) of the E8.5 wild-type embryo are indicated. The ectoplacental cone (epc) of the embryos in (A), (B), (D) and (E) was not removed during dissection, while the yolk sac was removed from the embryo in (F) for better visibility. Reichert’s membrane (r) is visible as a thin transparent sac surrounding the mutant embryos in (A), (B) and (D) but was removed during dissection from the embryos in (C) and (E).