Figure 3.
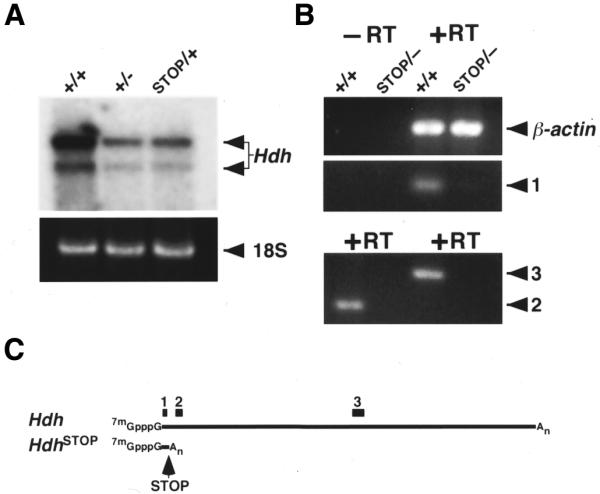
neostop suppresses Hdh expression. (A) Northern analysis of total RNA from adult brain obtained from a wild-type (+/+), Hdh heterozygote (+/–) and HdhSTOP/+ (STOP/+) mice is shown in the top panel. Hdh expression in the HdhSTOP/+ brain is equivalent to the expression in a Hdh+/– heterozygote. The two major Hdh mRNA transcripts (differing at their 3′ ends by the use of alternative polyadenylation sites) are indicated with arrows. A region of the RNA gel containing the 18S rRNA species (stained with ethidium bromide to control for sample loading and indicated with an arrow on the right) is shown in the bottom panel. (B) To determine if any transcripts were produced from the HdhSTOP allele, RT–PCR analyses were performed with total RNA isolated from wild-type (+/+) or HdhSTOP/– (STOP/–) E8.5 embryos using oligonucleotide primer pairs amplifying a region within exon 1 [1], exons 3–5 [2] and in the middle of the Hdh mRNA [3]. Reverse transcriptase was omitted from the cDNA synthesis reaction to control for DNA contamination (–RT), while amplification of β-actin cDNA was used as a control for RNA integrity and cDNA synthesis (β-actin). Note that PCR products corresponding to primer pairs 2 and 3 were not detected by ethidium bromide staining using the HdhSTOP/– cDNA template but were detected when using wild-type cDNA template. In contrast, a PCR product corresponding to β-actin was detected in equivalent amounts using the wild-type and HdhSTOP/– RNA samples. A PCR product corresponding to a putative truncated HdhSTOP RNA [1] was barely visible by ethidium bromide staining. (C) Schematics of the Hdh wild-type mRNA transcript and the putative truncated RNA transcript produced by the HdhSTOP allele (HdhSTOP). The positions of the PCR amplification products corresponding to the primer pairs 1, 2 and 3 are indicated by black rectangles.
