Figure 5.
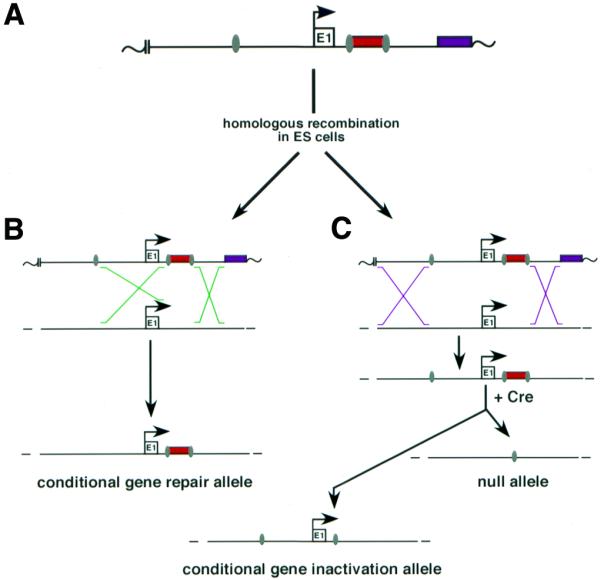
Diagram of a strategy to generate null, conditional inactivation and conditional gene repair alleles starting with the same targeting construct. (A) Two loxP sites (gray ovals) are shown flanking the neostop cassette (red rectangle) inserted within the target gene’s first intron and a third loxP site is located upstream of exon 1 (E1) and promoter elements. Transcriptional orientation is indicated with an arrow, and a thymidine kinase gene (for negative selection of transfected ES cells) is indicated with a purple rectangle. Plasmid sequences are indicated with wavy lines, and the restriction site used to linearize the target vector prior to electroporation is indicated with two vertical parallel lines. (B) Recombination occurring within the homology between the first two loxP sites and within the 3′ flanking homology will generate ES cells carrying a targeted conditional gene repair allele. (C) Recombination occurring within the flanking homology upstream of the first loxP site and within the 3′ homology will, in contrast, generate a targeted allele carrying all three loxP sites. In the presence of Cre, recombination between the first and third loxP sites will generate a null allele, while recombination between the loxP sites flanking the neostop cassette will generate a conditional gene inactivation allele (Discussion).
