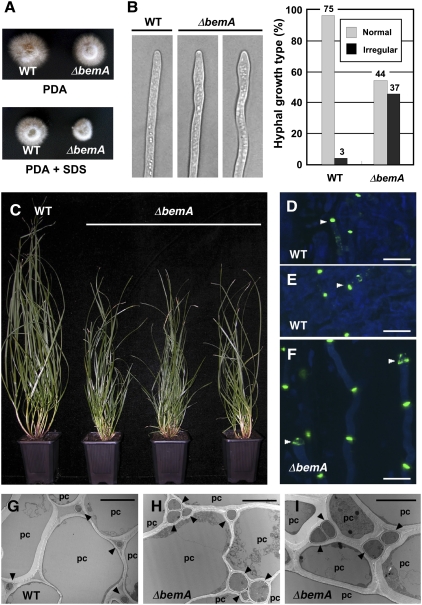
Fig. 5.
Axenic culture and in planta phenotype of E. festucae bemA mutant. (A) Colony morphology of WT Fl1 (WT) and ΔbemA mutant on PD agar (Upper) and PD agar with 0.01% SDS (Lower). (B) DIC images of WT Fl1 (WT) and ΔbemA mutant hyphal tips after growth on PD agar for 7 d and percentages of normal and irregularly shaped hyphal tips of both strains. Number of hyphae counted is given above each column. (C) Phenotype of perennial ryegrass plants infected with E. festucae WT Fl1 (WT) and ΔbemA mutant strains. Photograph was taken 12 wk after inoculation. (D–F) Confocal micrographs of aniline blue/WGA-AF488–stained hyphae growing in leaf sheath of 14-wk-old perennial ryegrass plants infected with WT Fl1 (WT; D and E) and ΔbemA mutant (F) strains. (Bar, 50 μm.) (G–I) Transmission electron micrographs of cross-sections of E. festucae Fl1 WT (WT; G) and ΔbemA mutant strain (H and I) hyphae (arrowheads) in the intercellular space of perennial ryegrass. pc, Plant cell. Photograph was taken 12 wk after inoculation. (Bar, 2 μm.)