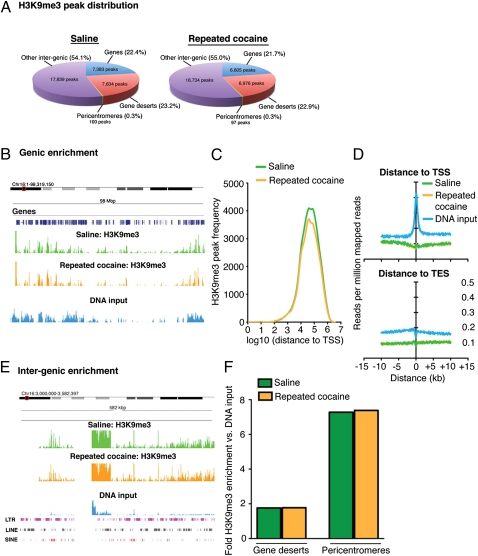
Fig. 2.
ChIP-Seq reveals significant enrichment of H3K9me3 throughout intergenic regions of the genome in NAc. (A) Mapping H3K9me3 peaks to several genomic features (Methods) reveals that the large majority of H3K9me3 peaks reside in intergenic genomic regions, whereas ≈20% associate with gene bodies. A small number of peaks reside within pericentromeres. No significant differences in peak distribution between saline- and cocaine-treated (24 h) animals were observed. (B) Although ≈20% of peaks reside within genic regions, H3K9me3 enrichment near gene bodies is low in comparison with DNA input. Image represents a Genome Browser snapshot of a highly genic 98-Mbp region of chromosome 16. (C) Analysis of H3K9me3 peak frequency in saline- and cocaine-treated animals demonstrates that the majority of peaks mapping to gene bodies are located more than 10 kbp from the TSS. Furthermore, H3K9me3 enrichment profiles for both treatment groups map below that of DNA input at both TSSs and TESs (D). (E) Consistent with peak distribution analyses, the H3K9me3 mark is heavily enriched throughout intergenic regions of the genome in comparison with DNA input. Image represents a 582-kbp region of the pericentromere of chromosome 16. Note the high abundance of genomic repeats overlapping with this region. (F) Although H3K9me3 is heavily enriched in noncoding regions of the genome, no significant differences were observed between saline and cocaine conditions within gene deserts or pericentromeres.