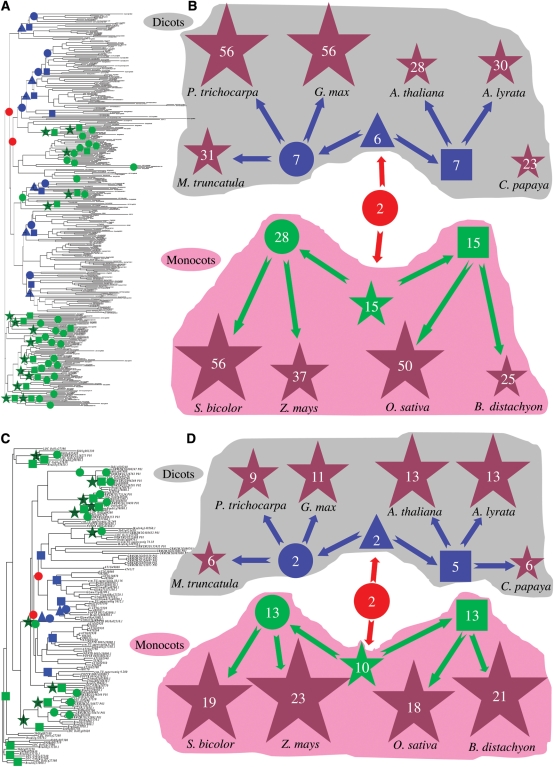
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic analysis and evolutionary dynamics of the Tau and Phi classes of the GST superfamily. (A and C) Phylogenetic analyses of the Tau and Phi subfamily members, respectively, in four monocot and six dicot plants. GST_N domain amino acid sequences were employed to construct phylogenetic trees using the bootstrap method with a heuristic search of the PAUP 4.0b8 program. The results were confirmed by the Bayesian analyses. Ancestral units were defined according to Shiu et al.64 Their enlarged phylogenetic trees and their analyses are shown in Supplementary Figs S2 and S3, respectively. (B and D) Evolutionary history of the Tau and Phi subfamily members in 10 organisms, respectively. Red circles represent the MRCA Tau/Phi units among all 10 organisms, blue triangles indicate the MRCA Tau/Phi units among dicot plants and green stars show the MRCA Tau/Phi units among monocot plants. Blue circles and squares represent the MRCA Tau/Phi units in Eurosid I (M. truncatula, P. trichocarpa and G. max) and Eurosid II (A. thaliana and A. lyrata), respectively. Green circles and squares show the MRCA Tau/Phi units between S. bicolor and Z. mays as well as between O. sativa and B. distachyon, respectively. Brown stars indicate the expanded Tau/Phi members in all 10 organisms. Grey and pink shadows in (B) and (D) indicate dicot and monocot plant species and their MRCAs, respectively.