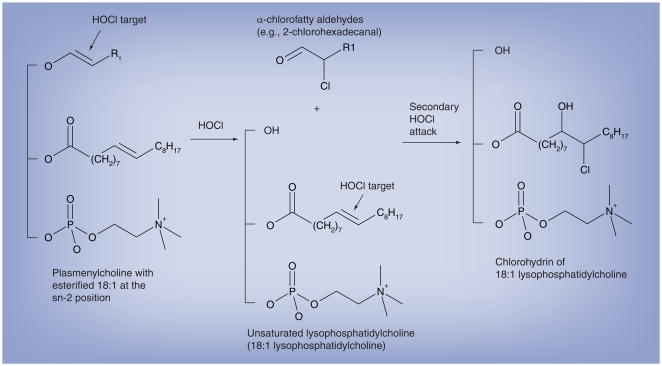
Figure 2. Chlorinated lipid products derived from HOCl targeting plasmenylcholine.
The vinyl ether bond of plasmalogens is targeted by HOCl resulting in the release of the masked aldehyde as an α-chlorofatty aldehyde. The other product of this reaction is an unsaturated molecular species of lysophosphatidylcholine. The alkene bond in the unsaturated molecular species of lysophosphatidylcholine is targeted by HOCl to yield a chlorohydrin molecular species. The vinyl ether bond is a preferred target for HOCl compared with the alkene, but the alkene is targeted following the removal of vinyl ether residues from the initial attack.
HOCl: Hypochlorous acid.