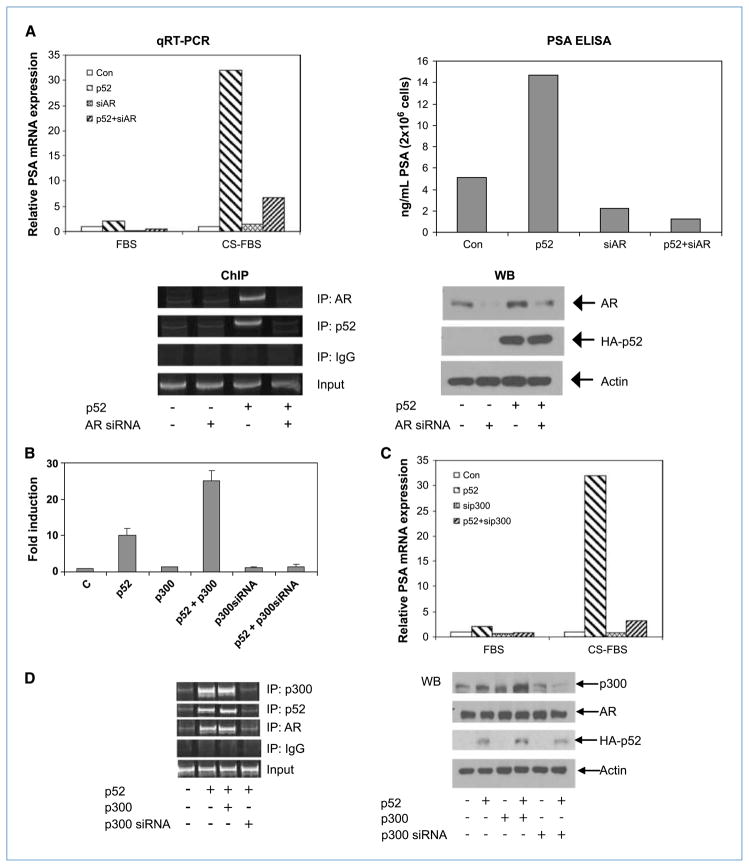
Figure 2.
p52-enhanced PSA expression is dependent on AR. LNCaP cells were transfected with plasmids expressing p52 or AR siRNA in FBS or CS-FBS. A, qRT-PCR: real-time PCR analysis was performed for PSA mRNA and results were expressed as fold change in relative mRNA expression. PSA ELISA: PSA protein expression was measured by ELISA in the supernatants. ChIP: ChIP assay was performed using AR, p52, or IgG antibodies. Recruitment of p52 to AREIII in the PSA promoter was abolished in the absence of AR. WB: expression levels of AR and p52 in the above experiments. B, p300 enhances PSA transactivation by p52. Androgen-deprived LNCaP cells were transfected with pGL3-PSA-Luc and plasmids expressing p52, p300, or p300 siRNA in CS-FBS for 48 h. Luciferase activities were measured. Columns, mean of triplicate samples; bars, SD. Three independent experiments were performed. C, p300 siRNA abolishes p52-induced increase in PSA mRNA. LNCaP cells transfected with plasmids expressing p52 or p300 siRNA were analyzed by qRT-PCR for PSA mRNA. D, p52 enhances p300 recruitment to the distal enhancer of PSA promoter. ChIP assay was performed using p300, p52, AR, or IgG antibodies and AREIII primers. WB: expression levels of HA-p52, AR, and p300 in the above experiments.