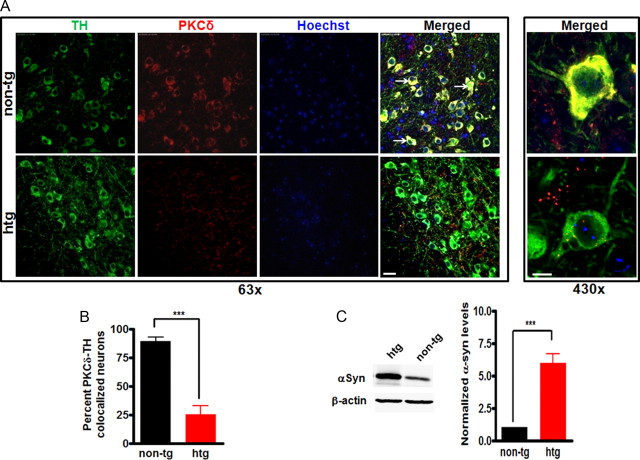
Figure 3.
Decreased PKCδ expression in nigral dopaminergic neurons in α-synuclein-overexpressing mice. A, Representative images of immunohistochemical analysis of PKCδ expression within nigral TH-positive neurons. Substantia nigra sections from nontransgenic control (non-tg) mice and αsyn-transgenic mice (htg) were stained with PKCδ polyclonal antibody (1:250 dilution) and TH monoclonal antibody (1:1800 dilution), followed by incubation with Alexa 568-conjugated (red; 1:1000) and Alexa 488-conjuated (green; 1:1000) secondary antibodies. Hoechst 33342 (10 μg/ml) was added to stain the nucleus. Confocal images were obtained using a Leica SP5 X confocal microscope system. Green, TH; red, PKCδ; blue, nucleus. The white arrows point to dopaminergic neurons with significant PKCδ staining. Scale bars: Left panel, 25 μm; right panel, 7.5 μm. Magnifications: Left panel, 63×; right panel, 430×. B, Quantification of the number of TH neurons containing colocalized PKCδ immunoreactivity was determined by blindly counting six fields and averaging. Values expressed as percentage of total TH neurons were mean ± SEM and representative for results obtained with three pairs of 6- to 8-week-old mice (***p < 0.001). C, To analyze the levels of αsyn in substantial nigra homogenates from transgenic mice overexpressing human wild-type αsyn and nontransgenic mice, substantial nigra homogenates were prepared from transgenic mice (htg) and nontransgenic mice (non-tg) and subjected to immunoblotting analysis of αsyn and β-actin. Representative immunoblot (left panel) and quantitation (right panel) of αsyn expression were shown. Approximately sixfold increase in αsyn expression in substantial nigra was found in transgenic mice. Data were shown as mean ± SEM; n = 6 (***p < 0.001).