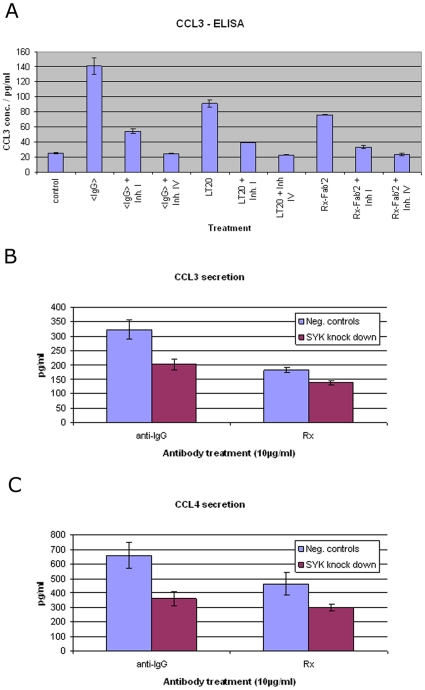
Figure 5. Repression of chemokine CCL3/4 induction caused by Syk inhibition and silencing.
(A) CCL3 secretion in SUDHL4 induced by anti-IgG antibodies and anti-CD20 antibodies and its inhibition by Syk inhibitors I and IV (Calbiochem) at 1 µM and 0,32 µM respectively. Bars represent mean of three replicates, including standard deviation (<IgG> = anti-IgG antibody, Inh. I = Syk inhibitor I, Inh. IV = Syk inhibitor IV, LT20 = murine anti-CD20 antibody, Rx-Fab'2 = F(ab')2 fragment of rituximab). Inhibition of CCL3 (B) and CCL4 (C) secretion in SUDHL4 induced by anti-IgG antibodies or rituximab after siRNA-mediated Syk silencing. Results represent at least three independent experiments. Students t-test for “Negative controls” vs. “SYK-knockdown”: for CCL3 secretion after anti-IgG treatment p = 6.8*10−7, Rx treatment p = 7.4*10−3. For CCL4 secretion after anti-IgG treatment p = 2.1*10−6, Rx treatment p = 2.5*10−4. (anti-IgG = anti-IgG antibody, Rx = rituximab, Neg. controls = RISCfree and Luciferase-siRNA transfections, respectively; SYK knock down = Syk-siRNA transfections).