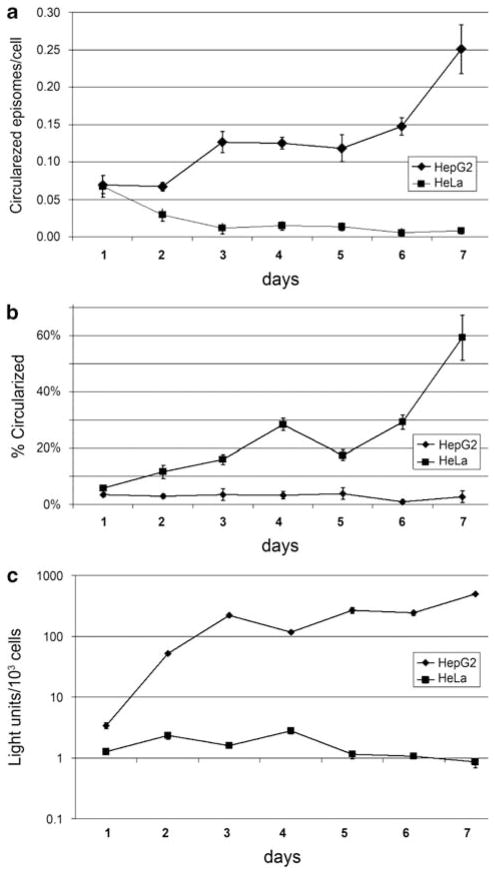
Figure 2.
Generation and stability of EBV episomes by Cre-mediated recombination in cultured cells. (a) HepG2 and HeLa cells were infected with HDAd-EBV.1x.hRluc at an MOI 2 IGU per cell and incubated in 2% calf serum containing media for 7 days. Cells were harvested daily and circularized vectors were assayed in isolated total nuclear DNA by quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR) with primers that detect circularized episomes specifically. Cell counts were determined by qPCR detecting the endogenous EEF2 gene. Error bars signify probable uncertainty calculated from standard deviation of triplicate qPCR samples. (b) Percentage of circularized vectors determined in HepG2 and HeLa cells over time. The same samples were subjected to qPCR to detect total vectors by targeting the EBNA sequence, contained in both circularized and unrecombined vectors. Percentage was determined by dividing detected circular vectors over total vectors. Error bars signify probable uncertainty calculated from standard deviation of triplicate qPCR samples, or the range of duplicates used in the last two samples for EBNA qPCR in HepG2 cells. (c) Luciferase assay results for extracts prepared at the indicated days post infection.