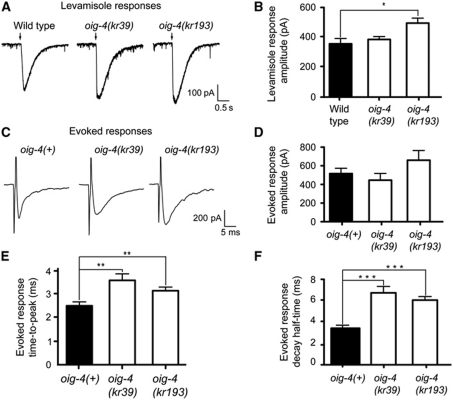
Figure 5.
L-AChRs are functional but diffusely distributed at the muscle membrane of oig-4 mutants. (A, B) L-AChRs are functional in oig-4 mutants. Response to pressure ejection of levamisole in voltage-clamped ventral muscle cells. Black arrows mark the 100 ms application onset for 5 × 10−4 M levamisole. The graph indicates the mean±s.e.m. of the levamisole-elicited current amplitude (366.7±36.6 for N2, n=7; 393.7±20.1 for oig-4(kr39), n=6, P=0.1605; 509.4±34.0 for oig-4(kr193), n=7, P=0.0175). (C–F) Evoked currents recorded from body-wall muscles after ventral nerve cord stimulation. (D) Evoked response amplitudes are 515.9±57.90 for oig-4(+), n=14 versus 445.0±72.76 for oig-4(kr39), n=7 and 659.2±104.5 for oig-4(kr193), n=11. The evoked response time-to-peak (E) and decay half-time (F) are increased in oig-4 mutants as compared to wild type (time-to-peak: 1.58±0.14 ms, n=13 for oig-4(+) versus 2.53±0.20 ms, P=0.0053, n=7 in oig-4(kr39) background, and 2.09±0.11 ms, P=0.0051, n=10 in oig-4(k193) background). Decay half-time: 3.45±0.22, n=15 for wild type and 6.49±0.55 ms, P=0.0007, n=8 for oig-4(kr39) and 6.07±0.35 ms, P=0.0002, n=11 for oig-4(kr193). Electrically evoked responses were obtained in an unc-49(e407);acr-16(ok789) background to eliminate currents due to GABAR and N-AChR activation. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001. Error bars are s.e.m.