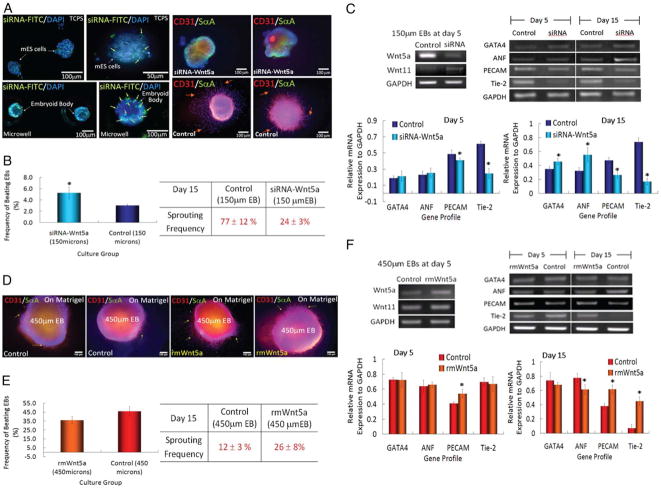
Figure 3.
Microwell-mediated control of EB size and cardiac and endothelial cell differentiation. (A) Immunocytochemical characterization of Wnt5a-siRNA transfection (green) EBs shows that transfected siRNA is delivered (Left). EBs are analyzed for the presence of endothelial cell marker CD31 (red) and cardiogenic marker sarcomeric-α-actinin (green). (B) Characterization of EB sprouting and beating frequency. (C) Gene expression of endothelial cell and cardiogenic differentiation marker from ES cells cultured in 150 μm diameter microwells. (D) Characterization of ES cell aggregates with the addition of recombinant mouse WNT5a in 450 μm diameter microwells. (Scale bar, 100 μm.) (E and F) Analysis of cardiogenic and endothelial cell differentiation by EB beating, vessel sprouting frequency, and gene expression. (n=3, * indicates P <0.05 compared to controls). Images reproduced with permission.24