Figure 5.
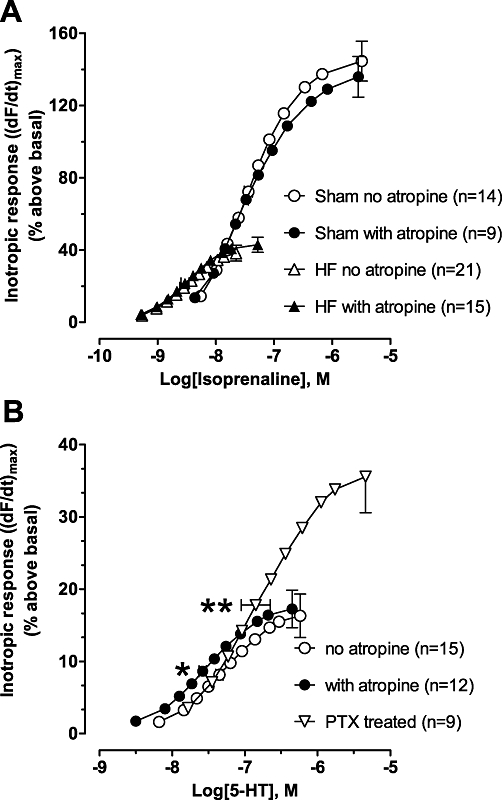
Atropine sensitizes heart failure (HF) ventricles to 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT)- but not isoprenaline-evoked inotropic effects. (A) Concentration–response curves of the inotropic response to isoprenaline in HF or sham-operated (Sham) papillary muscles in the absence or presence of 1 µM atropine. Inotropic response is expressed as increase of maximum dF/dt [(dF/dt)max] as % above basal. Basal Fmax (mN/mm2) was 5.1 ± 0.3 and 5.9 ± 0.4 for Sham and 4.8 ± 0.5 and 5.0 ± 0.3 for HF in the absence and presence of atropine, respectively. Data are mean ± SEM. (B) Effects of atropine (1 µM) and pertussis toxin (PTX) on the concentration-response curve of the inotropic response to 5-HT in HF papillary muscles. The 5-HT concentration-response curve for the PTX-treated group is the combined data of muscles with and without atropine from nine rats, because atropine did not significantly alter potency in PTX-treated rats. Basal Fmax (mN/mm2) was 5.4 ± 0.4 and 5.2 ± 0.5 in the absence and presence of atropine, respectively, and 4.9 ± 0.3 in the PTX-treated group. Data are mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05 versus no atropine. **P < 0.05 versus non-PTX treated.
