Figure 2.
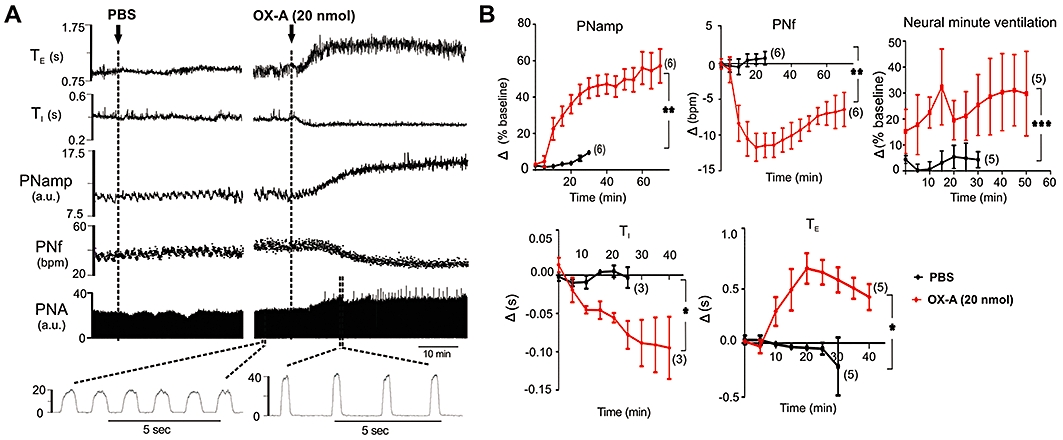
Effect of intrathecal injection of orexin A (OX-A)on phrenic nerve activity (PNA). (A) Representative trace of data from a recordings of rectified PNA (arbitrary unit, a.u.), phrenic nerve frequency (PNf), phrenic nerve amplitude (PNamp), inspiratory period (TI) and expiratory period (TE) before and after injection of phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) or OX-A. (B) Grouped time course effects of PBS (black) or OX-A (20 nmol) (red) on PNamp, PNf, neural minute ventilation, TI and TE. Following injection of OX-A there is an increase in PNamp associated with a bradypnoea that is due to both an increase in TE and a decrease in TI. There is an overall increase in neural minute ventilation over the period of the response. Values are expressed as mean ± standard error. Number of animals is shown in parentheses. bpm, beats per minute; ns, non-significant; ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05 compared with PBS.
