Figure 1.
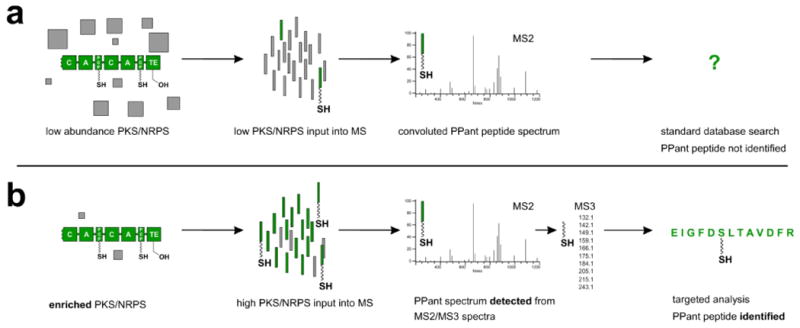
Approaches towards the proteomic identification of 4′-phosphopantetheinylated (PPant) peptides. (a) Traditional methods of proteomic analysis have difficulty in detecting PPant peptides due to their low abundance. In cases when PPant peptides are sampled by the spectrometer, spectra are often left unassigned due to weak fragmentation of the peptide backbone as well as convolution of MS2 spectra by PTM and parent mass ejection ions. (b) New approaches to the identification of PPant peptides investigated in the current study. Enrichment methods maximize the input of PPant peptides to the spectrometer. PPant peptides are initially detected by multistage fragmentation resulting in a characteristic MS3 pantetheine signature, or by a machine learning approach which detects PPant spectra based on their MS2 fragmentation patterns. Finally, PPant peptides are identified by a modified database search.
