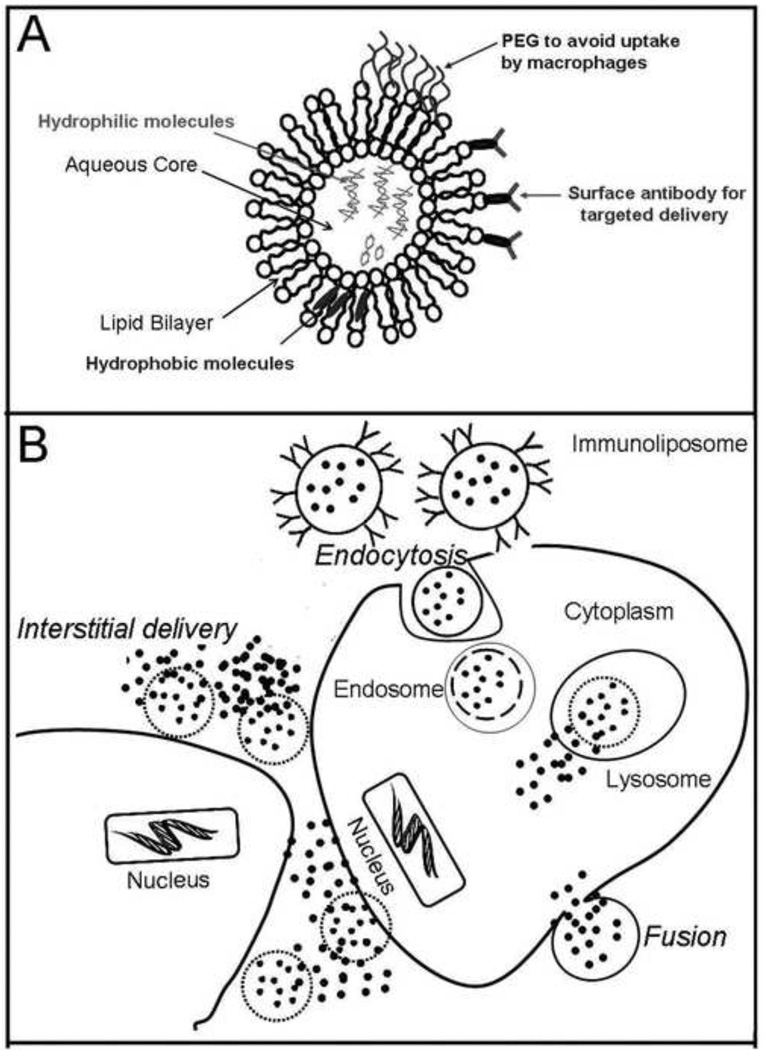
Figure 3.
(A) Illustration showing the liposome, consisting of a lipid bilayer that allows incorporation of hydrophobic molecules and a central aqueous core for hydrophilic molecules. A coat of polyethylene glycol (PEG) prevents uptake by macrophages and cells of the reticulo-endothelial system. Conjugation of antibody on the surface allows preferential targeting to cells of interest. (B) Liposomal contents are delivered into the target cells by fusion of the lipid bilayer with the cell membrane and by receptor or antibody mediated endocytosis. Liposomal contents are also released into the extracellular spaces in the vicinity of the target cell due to destabilization of the lipid bilayer in the interstitium.