Figure 4.
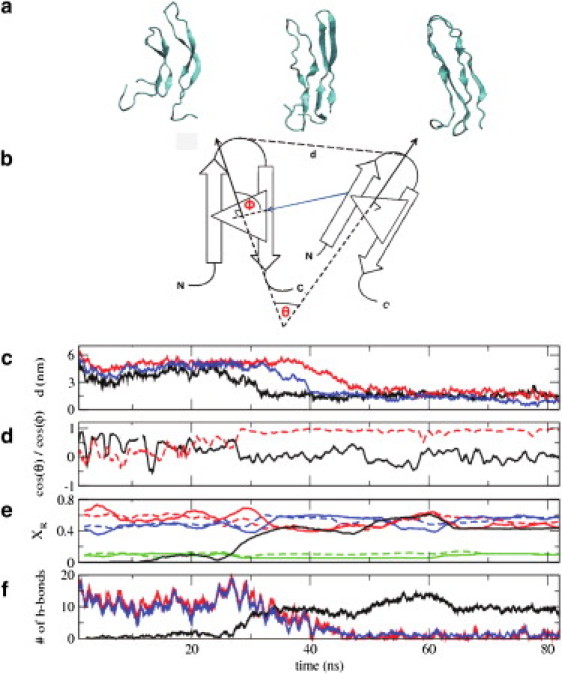
Dimerization of hIAPP monomers in solution. (a) Representative configurations along the dimerization pathway of two human amylin peptides in their β-hairpin conformation. The two β-hairpin structures interact by exchanging their intramolecular hydrogen bonds for intermolecular hydrogen bonds, resulting in a U-shaped β-sheet dimer structure. (b) Schematic representation of the distance and angles between two peptides that are used to characterize their dimerization (see below). (c) Distance (in nm) between residues 22 (the turn residues) of the two peptides as a function of time. Results are shown for three distinct trajectories started from three different initial configurations: (i) molecules at a distance of 5 nm, with a θ angle between the two peptides of 90° (shown in black); (ii) molecules at a distance of 6 nm, with a θ angle between them of 180° (shown in red); and (iii) molecules at a distance of 6.5 nm, with a θ angle between them of 0° (shown in blue). (d) For trajectory (i), the red dotted line shows cos(θ), the angle between the normals of the two molecules. (Black solid line) Cos(Φ), the angle between the line joining two peptides and one normal. (e) For trajectory (i), fraction of residues (XR) in a particular secondary structure. The secondary structure of a residue was assigned using the DSSP (67) approach. (Solid and dotted lines) Results for the two different peptides, respectively. (Red, blue, and green) Residues in β-sheet, random coil, and turn, respectively. (Solid black line) Fraction of residues exhibiting interstrand β-bridge joining two β-sheets. (f) For trajectory (i), (blue and red lines) number of main chain intrastrand hydrogen bonds for the two monomers; (black line) number of main chain interstrand hydrogen bonds.
