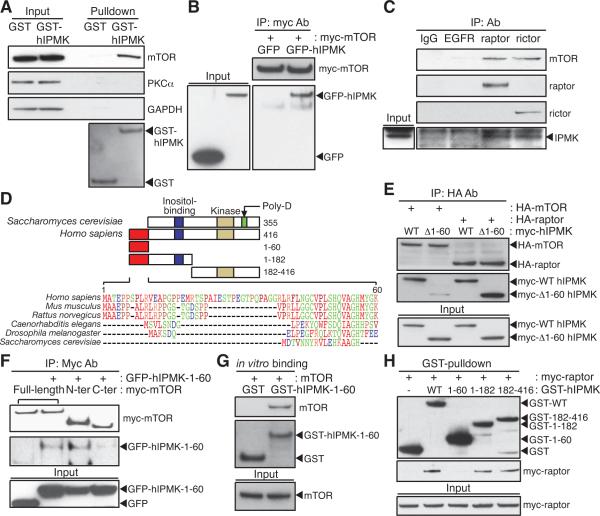
Figure 2. IPMK is an mTOR-associated protein.
(A) GST or GST-hIPMK was expressed in HEK293T cells, followed by pulldown and immunoblotting for endogenous mTOR. (B) GFP or GFP-hIPMK was co-transfected in HEK293T cells with myc-mTOR, and immunoprecipitates were analyzed by immunoblotting. (C) Lysates from IPMK-depleted MEFs stably expressing wild-type mouse IPMK were immunoprecipitated with indicated antibodies. (D) The unique sequence found in mammalian IPMK is aligned and indicated with a red box. Yeast IPMK-specific, polyaspartates sequence (Poly-D; green) and two conserved domains for inositol binding (blue) and kinase activity (yellow) are shown. IPMK fragments used for binding studies are shown in the schematic with the number of the amino acid sequence. (E) HA-mTOR or HA-raptor was co-transfected in HEK293T cells with wild-type or 1–60 deleted human IPMK (Δ1–60) constructs, followed by immunoprecipitation with HA-antibodies and immunoblotting. (F) Myc-wild-type mTOR, 1–1482 (N-ter) fragment, or 1328–2549 (C-ter) fragment was co-transfected in HEK293T cells with GFP or GFP-hIPMK-1–60, and myc-immunoprecipitates were analyzed by immunoblotting. (G) GST or GST-hIPMK-1–60 was incubated with mTOR purified from HEK293T cells. (H) GST or GST-hIPMK was co-transfected in HEK293T cells with myc-raptor, and myc-immunoprecipitates were analyzed by immunoblotting.