Fig. 4.
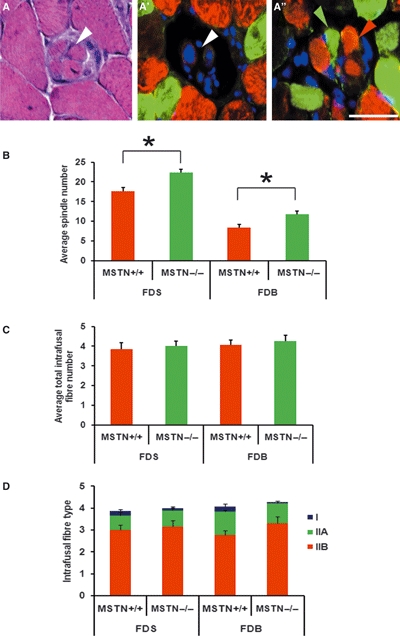
Myostatin deletion causes an increase in the number of muscle spindles but no changes in number of the intrafusal fibres or MHC-expressing fibres. (A) Haematoxylin and eosin staining. (A’–A’’) Double immunofluorescent labelling (right) against MHC IIa (green) and MHC IIb (red) stained with 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI, blue) showing the equatorial nuclear region (A’, white arrowhead) and the myosin heavy chain region at the polar end showing type IIa (A’’, green arrowhead) and type IIb (A’’, red arrowhead). Scale bar: 50 μm. (B) Average number of muscle spindles in the FDS and FDB muscles. Significant increases in muscle spindle number were observed in muscles from both mstn−/− (green bars) and age-matched mstn+/+ mice (red bars) (*P < 0.05). (C) Average total number of intrafusal fibres in muscle spindles from the FDS and FDB of mstn+/+ (red bars) and mstn−/− (green bars) mice. No significant differences were present. (D) The average number of MHC type I (blue), IIa (green) and type IIb (red) intrafusal fibres revealed no significant change in distribution in the mstn−/− compared to mstn+/+ mice.
