Fig. 5.
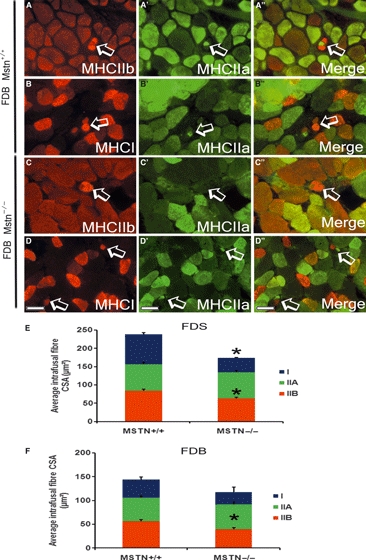
Myostatin deletion caused a decrease in the CSA of the intrafusal fibres but no changes in the histochemical properties of the spindle. (A-D) Double immunofluorescent staining for MHC IIa and IIb (A–A’’ and C–C’’) or IIa and I (B–B’’ and D–D’’) on transverse section of FDB muscle from mstn+/+ (A–B’’) and mstn−/− (C–D’’) highlighting intrafusal fibres (arrows). Scale bar: 50 μm. Quantification of the average CSA of MHC type I, IIa and IIb positive intrafusal fibres from the FDS (E) and FDB (F). (E) The average CSA of type I and type IIb intrafusal fibres was significantly smaller in the FDS muscle in the mstn−/− than in age-matched mstn+/+ mice (*P = 0.001). (F) The FDB muscle only displays a significant reduction in the average CSA of type IIb intrafusal fibres compared to mstn+/+ counterpart (*P = 0.005). All data are shown as mean ± SEM.
