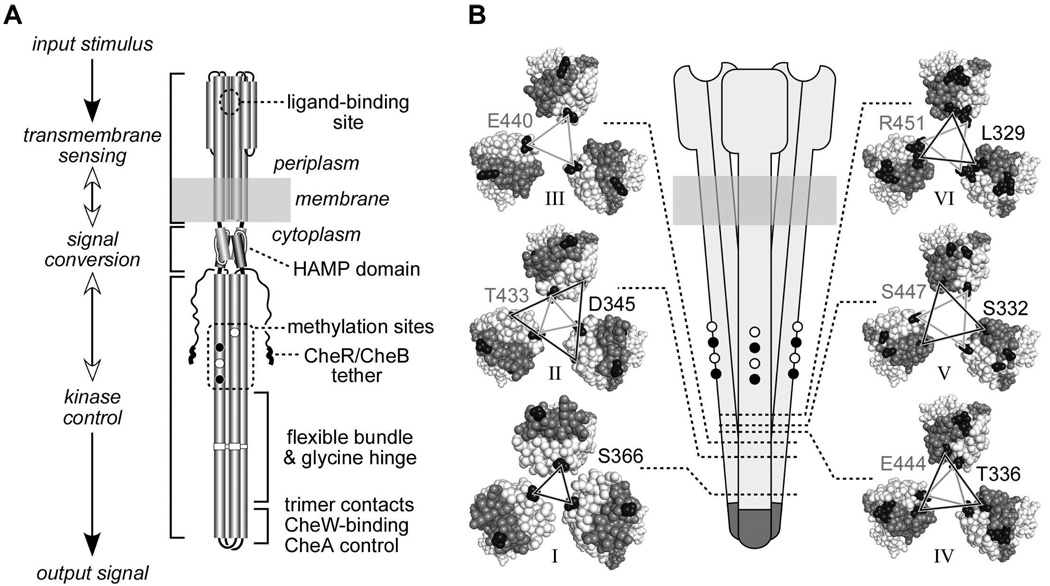
Fig. 1. Structural features of receptor molecules and trimers of dimers.
A. Functional architecture of Tsr and Tar homodimers. Cylindrical segments represent alpha-helices. Black circles represent methyl-accepting residues that are translated as glutamines, then deamidated to glutamate by CheB. CheR-CheB tether represents the C-terminal region to which the methylation enzymes bind.
B. Schematic representation of a trimer of dimers (center) and cross sections corresponding to the six levels, indicated by dotted lines and roman numbers, defined in Table 1. Cross section images were made with Pymol, viewing the trimer of dimers from the cytoplasm towards the membrane. Residues between the cytoplasmic tip and the corresponding level are hidden. Axial subunits (subunits that face the interior of the trimer at level I) are colored light gray; peripheral subunits are colored dark gray. Representative residues from each level that were substituted by cysteine residues are colored black. Lines connecting the cysteine-substituted residues are black when the residues reside in the N-helix of the subunit (helix running from the membrane to the cytoplasmic tip), and gray when the residues reside in the C-helix of the subunit (helix running from the cytoplasmic tip to the C-terminus). Residue identification uses a matching shading scheme and Tsr residue numbers, even though some replacements were made in Tar (see text and Table 1).