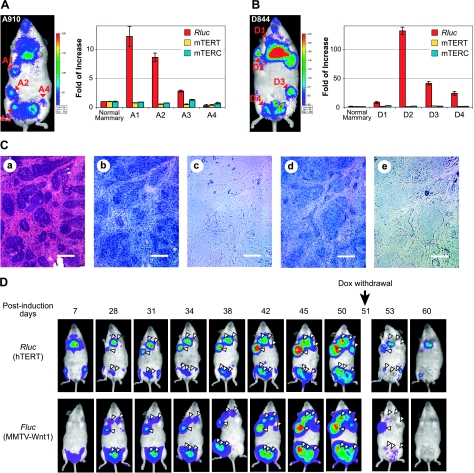
Figure 5.
hTERT activation in Wnt1-induced mammary tumors. A, B) Expression of transgenic hTERT reporter in mammary tumors. MTB (MMTV-rtTA)/TWNT (TetO–Wnt1)/hTERT triple-transgenic female mice A910 (60 d old) and D844 (40 d old) were put on a diet containing 2 mg/ml Dox and subjected to MNU treatment 7 d later. A910 (A) and D844 (B) mice were imaged at 36 and 46 d after MNU treatment, respectively, and tumors were dissected on the same days. Left panels: whole-body BLI of Rluc expression. Right panels: expression of Rluc and mTERT mRNAs, as well as mTERC in mammary tumors. Total RNAs were extracted from tumor biopsies and nearby normal mammary tissues. RNA levels were determined by qRT-PCR, normalized to 18S rRNA. Data are shown as fold of increase as compared to normal mammary tissue. C) RNA in situ hybridization of D2 tumor shown in B. H&E staining, riboprobes used (a), Rluc antisense (b), Rluc sense (c), mTERT antisense (d), and mTERT sense (e). Scale bars = 100 μm. D) Noninvasive imaging of mammary tumor development. MTB/TWNT/D-line triple-transgenic female mouse (81 d old) was treated with MNU after 1 wk of consuming a Dox-containing diet, followed by Dox withdrawal on d 51 postinduction. For each imaging session, the mouse was treated with 50 μg coelenteranzine in 100 μl via tail-vein injection, and Rluc images were captured, followed by IP injection of 150 μg d-luciferin and imaging of Fluc expression from the Wnt1 transgene. Triangles indicate positions of mammary tumors. Shift of the Fluc image on d 38 was from a slight movement of the mouse position during imaging. Weak Rluc signals around feet, rectal area, and oral nasal area likely resulted from autofluorescence of dried urine.