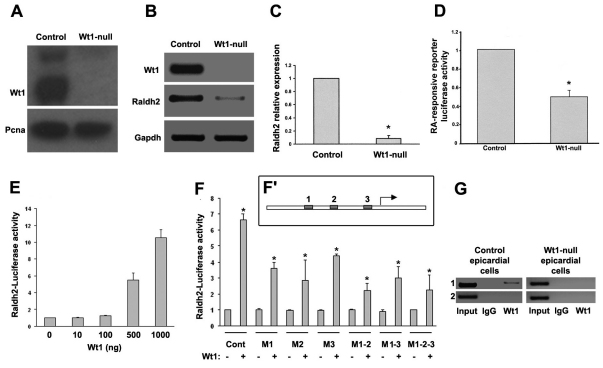
Fig. 2.
Wt1 is an activator of Raldh2 in epicardial cells.(A) Wt1 western blot in control and Wt1-null immortalised epicardial cells. (B,C) Raldh2 semi-qPCR (B) and qPCR (C) in control and Wt1-null immortalised epicardial cells. (D) RA-luciferase responsive reporter activity assay in control and Wt1-null immortalised epicardial cells. (E) The −KTS Wt1 isoform activates a Raldh2 promoter fragment containing the putative binding sites in a dose-dependent manner. (F,F′) Raldh2 promoter-luciferase mutagenesis assay. Reporter constructs, carrying single, double or triple mutations (see the schematic representation of the putative conserved Wt1-binding sites in the Raldh2 promoter, F′) were transiently co-transfected into epicardial cells with −KTS Wt1 expression vector. (G) ChIP assay in control and Wt1-null immortalised epicardial cells. Binding of Wt1 protein to the Raldh2 promoter is amplified with primers for Wt1 putative binding sites to Raldh2 promoter (1) or primers for regions upstream these sites (2). All asterisks indicate statistical significance (*P<0.05, 10 d.o.f.). Data are mean+s.e.m.