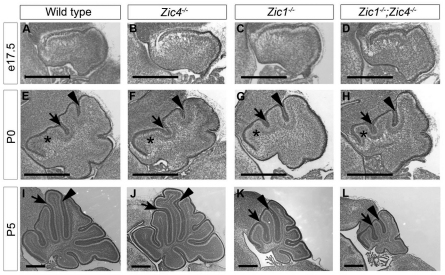
Fig. 3.
Zic1 and Zic4 cerebellar size and foliation defects arise postnatally. (A-D) Cresyl Violet stained sections showed no gross cerebellar morphological defects at E17.5 in single or double homozygous mutants (B-D) compared with wild type (A). (E-L) At P0, each genotype had the correct number of cardinal fissures, but while the Zic4−/− mutant (F) resembled wild type (E), in Zic1−/− (F) and Zic1−/−;Zic4−/− (G) mutants the preculminate fissure was shifted anteriorly and the anterobasal lobe (asterisk) was smaller than wild type. By P5, both the wild-type (I) and Zic4−/− mutant (J) cerebella had grown considerably, whereas Zic1−/− (F) and Zic1−/−;Zic4−/− (G) cerebella remained small. Black arrowheads and arrows indicate the primary and preculminate fissures, respectively. Scale bars: 500 μm.