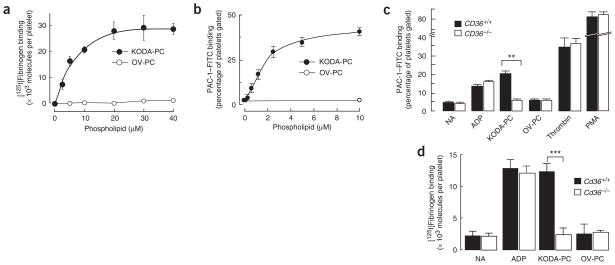
Figure 4.
oxPCCD36 activates platelet fibrinogen receptor integrin αIIbβ3 in a CD36-dependent manner. (a) Human platelets isolated by gel filtration were incubated with increasing concentrations of oxPCCD36 or OV-PC and αIIbβ3 activation was assessed on the basis of the binding of 125I-labeled fibrinogen. (b) Human platelets isolated by gel filtration were incubated with increasing concentrations of oxPCCD36 or OV-PC. After addition of agonist, FITC-labeled PAC-1 mouse monoclonal antibody (specific for activated integrin αIIbβ3) was added at a dilution of 1:100 and αIIbβ3 activation was assessed by FACS analysis. (c) Human platelets were isolated from CD36+/+ or CD36−/− donors and analyzed for αIIbβ3 activation as in b. The final concentrations of stimuli used were 10 μM ADP, 20 μM lipid oxidized phospholipids, 0.5 U/ml thrombin and 10 nM PMA. NA, no additions. (d) Washed platelets from wild-type or Cd36−/− mice were incubated with 10 μM ADP or 20 μM synthetic oxidized phospholipids, and platelet activation was assessed by 125I-labeled fibrinogen binding. NA, no additions. Results represent the mean ± s.d. of three independent experiments. Statistical significance was determined by t-test: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. See Supplementary Methods for details.