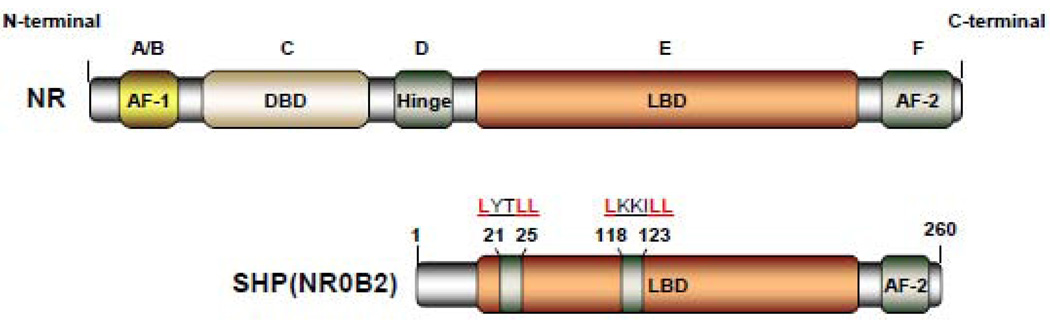
Figure 1. Domain structure of the orphan nuclear receptor SHP.
Classical nuclear receptor (NR) contains five major functional domains: the N-terminal ligand-independent transactivation domain (A/B domain), the DNA binding domain (DBD or C domain), hinge region (D domain), the C-terminal ligand-binding domain (LBD or E domain), and the ligand-dependent transactivation domain (AF2 or F domain). Compared to the classical NRs, SHP contains the dimerization and LBD domain, but lacks the conserved DBD. SHP represses the transcriptional activities of its targets gene by utilizing two functional LXXLL-related motifs (also called NR-boxes) which are located in the putative N-terminal helix 1 of the LBD and in the C-terminal region of helix 5.