Table 1.
Guide to evaluation and selection of patients for subcutaneous injection immunotherapy/sublingual immunotherapy (SCIT/SLIT) to aero-allergens for allergic rhinitis (#contraindications for specific allergen immunotherapy to aero-allergens).
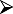 Evaluate symptoms and response to first-line pharmacotherapy (including compliance, nasal spray technique) Evaluate symptoms and response to first-line pharmacotherapy (including compliance, nasal spray technique) |
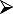 Quality of life significantly affected? Quality of life significantly affected? |
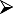 Co-existing local nasal airway pathology such as polyps, deviated septum Co-existing local nasal airway pathology such as polyps, deviated septum |
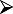 Evaluate allergenic trigger from history, e.g. timing of symptoms in the calendar year for hay fever, in case of perennial rhinitis for other factors such as exposure to moulds, animal dander, occupational factors, etc. Evaluate allergenic trigger from history, e.g. timing of symptoms in the calendar year for hay fever, in case of perennial rhinitis for other factors such as exposure to moulds, animal dander, occupational factors, etc. |
 Has the patient followed allergen avoidance measures where appropriate? Has the patient followed allergen avoidance measures where appropriate? |
 Consider environmental factors, both indoor as well as outdoor Consider environmental factors, both indoor as well as outdoor |
 Asthma Asthma |
| ○Mild, moderate# or severe# |
| ○Asthma treatment |
| ○Requirement for short acting β2 agonist per day |
| ○ Recent asthma attacks |
| ○ Nocturnal symptoms |
| ○ Compliance |
| ○ PEFR charts |
| ○ FEV1 |
 Other co-morbid factors and medications Other co-morbid factors and medications |
| ○ Underlying cardiac and respiratory disorders# |
| ○ Beta blockers#, ACE inhibitors# |
| ○ Systemic autoimmune conditions#, oral/parenteral steroids#, immunosuppressive drugs# |
| ○ Pregnancy# |
ACE: angiotensin-converting enzyme; FEV1: forced expiratory volume in 1 s; PEFR: peak expiratory flow rate.
