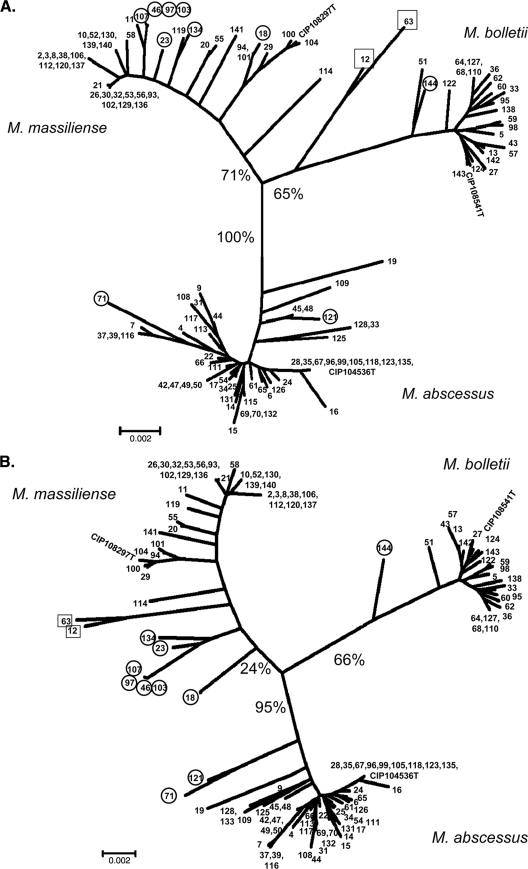
Fig. 3.
Trees constructed from concatenated sequences. (A) Concatenated MLSA sequences. (B) Concatenated MLSA + rpoB sequences. The trees for all studied strains (n = 123) were generated by using the neighbor-joining method. Bootstrap support values (%) are indicated for each node. Each isolate is indicated by its number in our collection. CIP type strains also are indicated. Boxes indicate isolates with discordant rpoB-based identification (see Table 3 for further details). Note that isolates 12 and 63 are located on the M. bolletii branch of the MLSA tree (A) and on the M. massiliense branch of the MLSA + rpoB tree (B).