Figure 8. Propagation of action potentials along distal fibres influences the distribution of surface potentials.
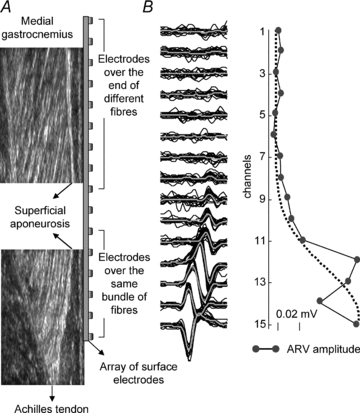
A illustrates how the fascicles of MG muscle were distributed below the array of surface electrodes. Electrodes in the distal portion of the array cover the same MG fibres, allowing the same intramuscular potential to be detected from different locations on the surface of the skin because of the propagation of action potentials. Proximal electrodes are located on the superficial extremity (aponeurosis) of different MG fascicles and are unlikely to have recorded from the same muscle fibres. B, raw surface action potentials (and their average; thick grey lines) triggered with the firing pattern of one motor unit identified in the MG90% location. Note the delay between potentials and the phase inversion for the potentials with similar amplitude in channels 14 and 15. C shows the sparse distribution of ARV amplitude for the averaged potentials shown in B.
