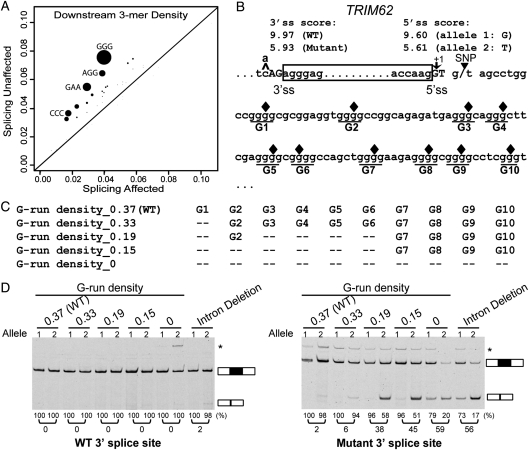
Figure 5.
The upstream 3′ splice site and downstream intronic poly-G runs function redundantly to protect a TRIM62 exon from its 5′ splice site polymorphism. (A) Trinucleotide motifs enriched within the 100 bp intronic region downstream of the ‘splicing unaffected' exons as compared with the ‘splicing affected' exons. X-axis shows motif density in ‘splicing affected' exons. Y-axis shows motif density in ‘splicing unaffected' exons. The size of each dot is proportional to the negative log of the P-value for motif enrichment. The nucleotide sequences of motifs with Bonferroni-corrected P-values of <0.05 are shown. (B) The nucleotide sequence of the TRIM62 exon and its flanking intronic regions. Box frame indicates the exon. Ten poly-G runs in the 100 bp downstream intron are underlined and denoted as G1-G10. Filled diamonds represent the positions where single-nucleotide mutations are introduced to disrupt individual poly-G runs. (C) Schematic diagrams of mutant minigene constructs with serial disruptions of poly-G runs. (D) Results of TRIM62 minigene experiments by site-directed G-to-C disruptions of poly-G runs. Disruptions of poly-G runs in the minigene constructs containing the wild-type 3′ splice site have no impact on exon splicing (left panel). Disruptions of poly-G runs in the minigene constructs containing the mutant (weakened) 3′ splice site significantly reduce the exon inclusion level of the TRIM62 exon. In the ‘Intron Deletion' constructs, only the first 6 intronic nucleotides within the 5′ splice site of the TRIM62 exon are kept when inserted into the basic pI-11-H3 minigene vector. The vector sequence that now serves as the intronic sequence immediately downstream of the TRIM62 5′ splice site contains basic splicing signals, i.e. a strong branch point and the 3′ splice site for the downstream constitutive exon. In all gel pictures, the number below each lane represents the percent exon inclusion level estimated by the fluorescently labeled RT–PCR. Asterisk denotes PCR products of unexpected sizes resulting from the usage of cryptic splice sites as confirmed by sequencing. 5′ ss, 5′ splice site; 3′ ss, 3′ splice site.