Fig 10.
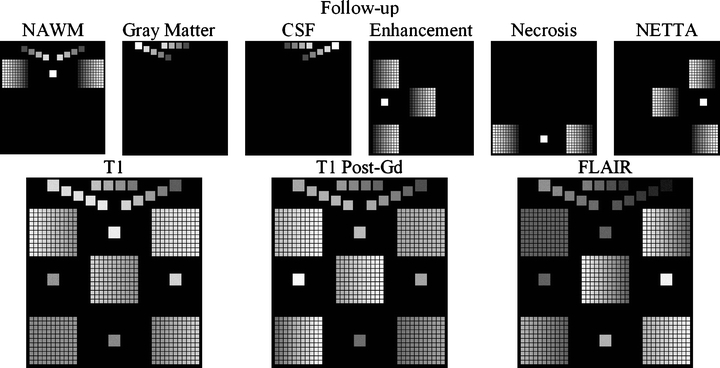
Construction of the follow-up change phantom. As in Figure 9, the membership volumes for the desired phantom (top row) are used to generate the synthetic pulse sequences (bottom row). Note the difference in orientation of the gradation within the grids at each time point. The result is a broad range of starting and stopping membership values over each grid/dual-tissue class.
