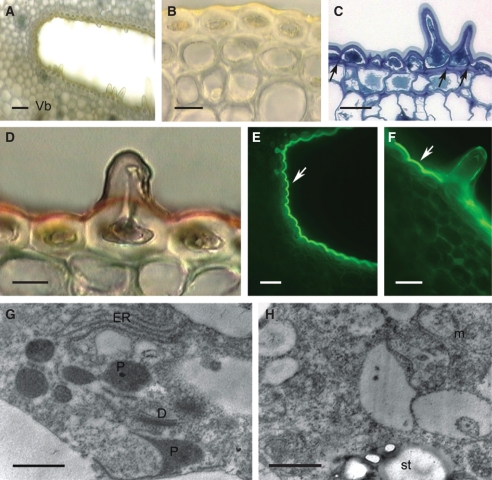
Fig. 4.
Histology and ultrastructure of spur of A. curvifolium: (A–F) light micrographs; (G,H) transmission electron micrographs. (A) Hand-cut section of spur wall showing epidermis with secretory hairs, underlying tissues and vascular bundle. Scale bar =50 µm. (B) Hand-cut section of spur treated with IKI and showing glabrous, thick-walled epidermal cells from proximal part of spur and thick-walled subepidermal cells. Scale bar = 20 µm. (C) Detail of thick-walled epidermis with secretory hairs and thick cuticle, together with subepidermal cells. Note that walls are pitted (arrows). Scale bar = 25 µm. (D) Cuticle covering glabrous epidermal cells stains intensely with Sudan III, but that covering the secretory hairs stains only slightly. Scale bar =10 µm. (E) Thick-walled epidermal cells from distal part of spur treated with auramine O and showing thick, strongly fluorescent cuticle (arrow). (F) Secretory hair with weakly fluorescent cuticle following staining with auramine O. Note that elsewhere, the cuticle fluoresces strongly (arrow). (E,F) Scale bars = 25 µm. (G) Detail of cytoplasm with dictyosomes, ER and irregular plastid profiles. (H) Secretory cell showing mitochondria and plastid with starch grains. (G,H) Scale bars = 1 µm. Abbreviations: see Fig. 1.