Fig. 1.
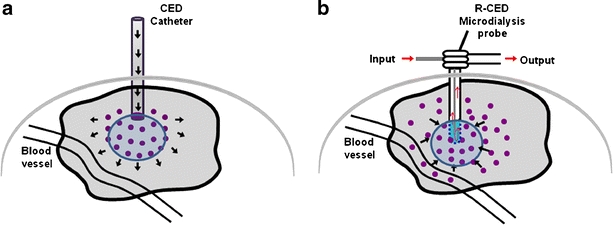
Schematic illustration of fluid movement in the brain under the influence of CED or R-CED. a A CED catheter is implanted into the brain, and a solution is perfused under a positive pressure (black arrows). The therapeutic solution convects in response to the pressure field. This allows permeation and distribution of the therapeutic agent contained in the solution into the region of interest. b To remove fluid from the brain, a hyperosmotic solution is perfused into the brain using a microdialysis probe. The microdialysis membrane separates the hyperosmotic perfusate from the brain interstitial. Fluid then flows from the blood into the ISF and towards the microdialysis probe as diagrammed with the black arrows. The fluid then exits through the output tube of the probe.
